Variable partitioning scheme is also know as dynamic partitioning.Variable partitioning is part of the contiguous allocation technique. It is used to alleviate the problem faced by fixed partitioning. As opposed to fixed partitioning, in variable partitioning, partitions are not created until a process executes. At the time it is read into main memory, the process is given exactly the amount of memory needed. This technique, like the fixed partitioning scheme previously discussed have been replaced by more complex and efficient techniques.
The amount of space allocated to a process is the exact amount of space it requires. Thus it does not suffers from internal fragmentation. For example,the initial partition assignment in variable partitioning is shown in figure. This example uses main memory of 1MB. Initially, main memory is empty except for the operating system (100 k). The first four processes A, B, C and D are loaded in, starting where the OS ends, and occupy just enough space for each process. As a result, a hole is left at the end of the memory & this hole is too small for fifth process. (Process E that requires 150K of memory).
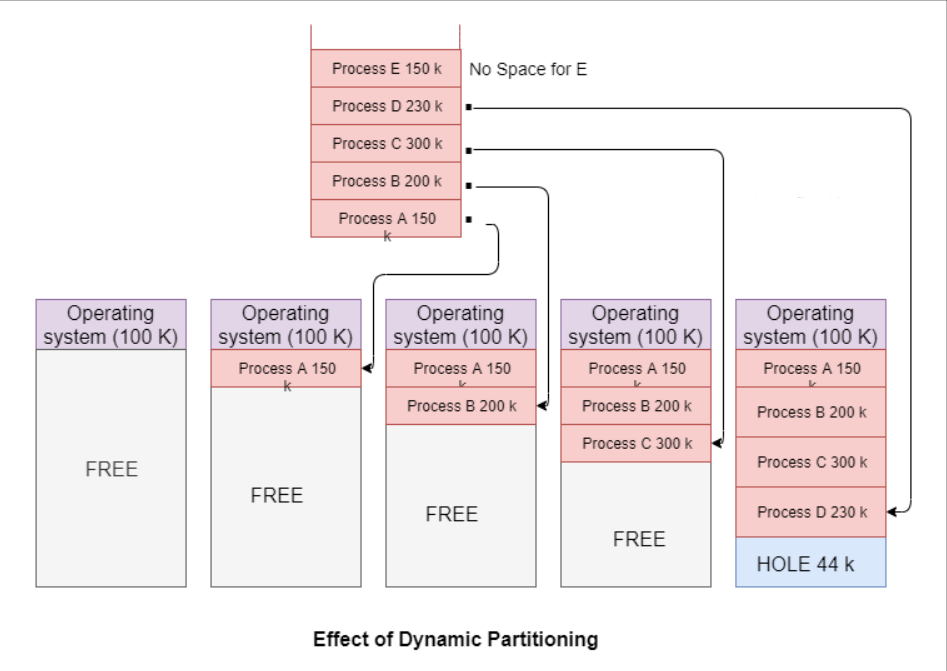
At some point, none of the processes in the memory is ready. The operating system therefore swaps out process B which provides sufficient room to load a new process E. As process E is smaller than process B, another small hole is created.
Methods of Operation in Multiple Variable Partition Allocation
- In variable partition, a set of holes, of various sizes, is scattered throughout memory at any given time.
- When a process arrives and needs memory, the OS searches for a hole that is large enough for this process
- If the hole is too large, it is divided into two parts. One part is allocated to the arriving process and the other is returned to the set of holes.
- For each partition allocated, the information like base address of partition, size and its status (ALLOCATED) is added to partition description table (PDT).
- When a process terminates, it releases its block of memory. This block of memory is placed back in the set of holes.
- If the new hole is adjacent to other holes, these adjacent holes are merged to form one larger hole.
- No Internal Fragmentation: In variable Partitioning, space in main memory is allocated strictly according to the need of process, hence there is no case of internal fragmentation. There will be no unused space left in the partition.
- No restriction on Degree of Multiprogramming: More number of processes can be accommodated due to absence of internal fragmentation. A process can be loaded until the memory is empty.
- No Limitation on the size of the process: In Fixed partitioning, the process with the size greater than the size of the largest partition could not be loaded and process can not be divided as it is invalid in contiguous allocation technique. Here, In variable partitioning, the process size can’t be restricted since the partition size is decided according to the process size.
- Difficult Implementation: Implementing variable Partitioning is difficult as compared to Fixed Partitioning as it involves allocation of memory during run-time rather than during system configure.
- External Fragmentation: There will be external fragmentation inspite of absence of internal fragmentation.
Compaction
- External fragmentation can be resolved through compaction
- Shuffles the memory contents to put all free memory together in one block
- Compaction algorithm is expensive, but so is not making efficient use of memory, especially with a lot of concurrent processes